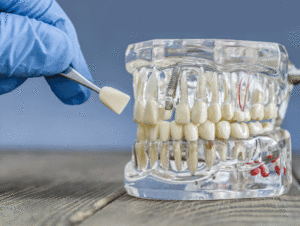
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a serious infection that affects the tissues supporting the teeth. It begins as gingivitis, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding gums, and can progress into periodontitis, which causes irreversible damage to the bone and connective tissue. Many individuals do not recognize the early signs, making regular dental visits crucial for early detection and prevention. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and genetic predisposition contribute to the development of this disease. Left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to tooth loss, receding gums, and chronic bad breath. Beyond oral health, research has linked gum disease to serious systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation in other parts of the body. Maintaining periodontal health is essential for preserving both dental function and overall well-being.
The effects of periodontal disease extend beyond the mouth, impacting quality of life and daily comfort. Patients with advanced periodontitis may experience difficulty eating, sensitivity, and persistent discomfort. Additionally, the aesthetic consequences of gum disease, including gaps between teeth and gum recession, can affect self-confidence. Regular professional cleanings, along with proper at-home care, can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Implementing a proactive oral hygiene routine that includes brushing, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help prevent gum disease. Visiting a dental professional at the first sign of gum inflammation can prevent the need for more invasive treatments. Understanding the risks associated with periodontal disease highlights the importance of early intervention and ongoing care. By prioritizing gum health, individuals can protect both their smiles and their overall health for years to come.